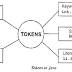
A token is a group of
characters that logically belong together. The programmer can write a program
by using tokens. C++ uses the following types of tokens.
Keywords, Identifiers, Literals, Punctuators, Operators.
Keywords, Identifiers, Literals, Punctuators, Operators.
1. Keywords
These are some reserved words in C++ which
have predefined meaning to compiler called keywords. It is discussed in
previous section.
2. Identifiers
Symbolic names can be used in C++ for various
data items used by a programmer in his program. A symbolic name is
generally known as an identifier. The identifier is a sequence of
characters taken from C++ character set. The rule for the formation of an
identifier are:
·
An
identifier can consist of alphabets, digits and/or underscores.
·
It must
not start with a digit
·
C++ is
case sensitive that is upper case and lower case letters are considered
different from each other.
·
It
should not be a reserved word.
3. Literals
Literals (often referred to as constants) are
data items that never change their value during the execution of the program.
The following types of literals are available in C++.
·
Integer-Constants
·
Character-constants
·
Floating-constants
·
Strings-constants
Integer Constants
Integer constants are
whole number without any fractional part. C++ allows three types of integer
constants.
Decimal integer constants : It consists of sequence of digits and should not begin with 0 (zero). For example 124, - 179, +108.
Octal integer constants: It consists of sequence of digits starting with 0 (zero). For example. 014, 012.
Hexadecimal integer constant: It consists of sequence of digits preceded by ox or OX.
Decimal integer constants : It consists of sequence of digits and should not begin with 0 (zero). For example 124, - 179, +108.
Octal integer constants: It consists of sequence of digits starting with 0 (zero). For example. 014, 012.
Hexadecimal integer constant: It consists of sequence of digits preceded by ox or OX.
Character constants
A character constant in C++ must contain one
or more characters and must be enclosed in single quotation marks. For example
'A', '9', etc. C++ allows nongraphic characters which cannot be typed directly
from keyboard, e.g., backspace, tab, carriage return etc. These characters can
be represented by using an escape sequence. An escape sequence represents a
single character.
Floating constants
They are also called real constants. They are
numbers having fractional parts. They may be written in fractional form or
exponent form. A real constant in fractional form consists of signed or
unsigned digits including a decimal point between digits. For example 3.0,
-17.0, -0.627 etc.
String Literals
A sequence of character enclosed within double
quotes is called a string literal. String literal is by default (automatically)
added with a special character ‘\0' which denotes the end of the string.
Therefore the size of the string is increased by one character. For example
"COMPUTER" will re represented as "COMPUTER\0" in the
memory and its size is 9 characters.
4. Punctuators
The following characters are used as
punctuators in C++.
Brackets [
]
|
Opening and closing
brackets indicate single and multidimensional array subscript.
|
Parentheses (
)
|
Opening and closing
brackets indicate functions calls,; function parameters for grouping
expressions etc.
|
Braces { }
|
Opening and closing
braces indicate the start and end of a compound statement.
|
Comma ,
|
It is used as a
separator in a function argument list.
|
Semicolon ;
|
It is used as a
statement terminator.
|
Colon :
|
It indicates a labeled
statement or conditional operator symbol.
|
Asterisk *
|
It is used in pointer
declaration or as multiplication operator.
|
Equal sign =
|
It is used as an
assignment operator.
|
Pound sign #
|
It is used as
pre-processor directive.
|
5. Operators
Operators are special symbols used for
specific purposes. C++ provides six types of operators. Arithmetical operators,
Relational operators, Logical operators, Unary operators, Assignment
operators, Conditional operators, Comma operator.











0 comments:
Post a Comment